Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA or ELASA) refers to a qualitative and quantitative assay in which a soluble antigen or antibody is bound to a solid-phase carrier such as polystyrene, and the immune reaction is performed using specific binding of the antigen and antibody.
This assay technique is mainly used for quantitative or qualitative detection of antibodies, proteins, cytokines, hormones, etc. in samples.

Binding an antigen or antibody to the surface of some solid phase carrier (e.g., an enzyme plate) and maintaining its immunological activity. The antigen or antibody is conjugated to an enzyme to form an enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody, which retains both its immune activity and the enzyme activity.
The specimen under test (to determine the antibody or antigen in it) and the enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody are then reacted with the antigen or antibody on the surface of the solid-phase carrier in different steps. The antigen-antibody complex formed on the solid-phase carrier is separated from other substances by washing, and finally the amount of enzyme bound to the solid-phase carrier is proportional to the amount of the substance under test in the specimen. After adding the substrate of the enzyme reaction, the substrate is catalyzed by the enzyme to change into colored product, and the amount of the product is directly related to the amount of the tested substance in the specimen, so it can be analyzed qualitatively or quantitatively according to the shade of the color reaction. Because of the high catalytic efficiency of the enzyme, the reaction effect can be greatly amplified, thus making the measurement method highly sensitive.
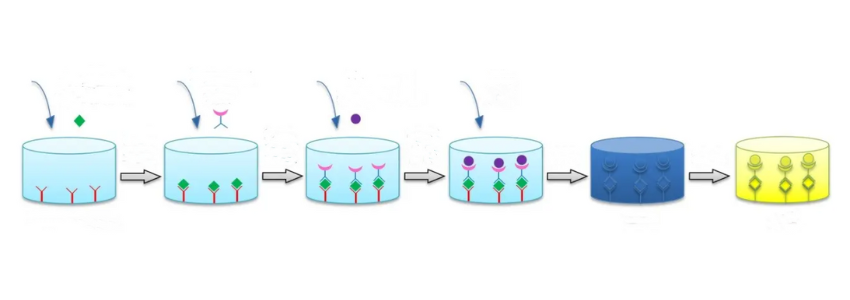

In the process of practical application, people also according to the specific situation of the flexible use of basic detection principles, developed a variety of ELISA assay types, the current common types are: sandwich method, direct method, indirect method, competition method.
Sandwich method: The double antibody sandwich method is suitable for the determination of bivalent or bivalent macromolecules, but not for small molecule antigens. A specific antibody (capture antibody) is attached to a solid phase carrier to form a solid phase antibody. After washing to remove unbound antibodies and impurities, the sample to be tested is added, and the specific antigen in the sample binds to the solid phase antibody to form a solid phase antigen-antibody complex. The sample is washed to remove other unconjugated material. Add the enzyme-labeled antibody (detection antibody). After the antigen on the solid phase immune complex binds to the enzyme-labeled antibody, wash the unbound enzyme-labeled antibody thoroughly and add the substrate for reaction color development.
The reaction pattern of the double antibody sandwich method for measuring antibodies is similar to that of measuring antigens, where specific antigens are used to coat and prepare enzyme conjugates to detect the corresponding antibodies.
Direct method: It is mainly used for the determination of antigens. The antigen is attached to the solid phase carrier and washed to remove unbound antigen and impurities. Then the enzyme-labeled antibody is added and the unbound enzyme-labeled antibody is washed thoroughly after the antigen on the solid-phase immune complex is bound to the enzyme-labeled antibody. At this point, the amount of enzyme on the solid phase correlates with the amount of antigen examined in the specimen, and then the substrate is added to the reaction for color development.
Indirect method: The antigen is conjugated to the solid phase carrier to form the solid phase antigen. The unbound antigen and impurities are removed by washing. Add specific primary antibody and solid phase antigen to form a solid phase antigen-antibody complex. After washing, the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody is added. The antibody in the solid phase immune complex binds to the enzyme secondary antibody, thereby indirectly labeling the enzyme. After washing, the substrate is added to the reaction for color development.
Competition method: This method is usually used to detect small molecules such as semi-antigens, hormones, drugs, etc. The free antigen to be detected competes with the antigen immobilized on the solid phase carrier for the same limited amount of antibody, when the more free antigen in the sample, the more antibody can be bound, while the solid phase antigen can only bind a smaller amount of antibody. Washing removes the antigen-antibody conjugate from the sample, leaving only the solid phase antigen-antibody conjugate.

JYBIO ELISA plate is specially used for all kinds of ELISA experiments, the plate is made of medical grade polystyrene, because the hydrophobic part between protein and polystyrene surface can adsorb each other, the soluble antigen or antibody can effectively bind to the solid phase carrier to ensure the smooth conduct of the experiment. In addition, the Amgente plate complies with ANSI-SBS standard, the CV value between wells is <5%, and there is no DNase and RNase, no endotoxin, absolute quality assurance!

Contact: Mr.Jybio
Phone: +86 15879982901
Tel: 028-87033305
Email: info@jybioscience.com
Add: No.68 Julong Road,Wuhou District Chengdu,Sichuan,CN
We chat
